Squatting is one of those activities that we despise but yet offers a plethora of advantages. Squats are much more than a leg workout. To squat weight, your legs do the majority of the work.
However, when your upper body balances the bars, your abdominal and lower back muscles must stabilize your torso.
From head to toe, squats engage your entire body. As a result, you'll be able to lift a greater weight.
Squats than with other exercises and why they're better for building total strength and muscle. Squats work on your thighs, calves, lower back, abs, and arms.
Athletes squat every day because squatting has been demonstrated to have a direct impact on your body's power - your capacity to overcome gravity quickly – according to research.
As a result, having strong squatting muscles leads to more strength and faster sprinting. Squats are pretty beneficial even if you are not a professional athlete.
You'll feel the heat in your quadriceps, glutes, and calves, but you'll also feel it in your back if your form is improper when doing squats. It can also stop you from going to the gym for an extended period if it grows worse.
Hip discomfort can also be the source of lower back pain. Squats, on the other hand, have been known to bring unwelcome low back pain.
While the squat works the lower back muscles, persistent pain and overuse damage can develop if it is the most targeted location during the squat.
Here are some common mistakes that could injure your back during squats:
4 Tips When Doing Squats
1. Your elbows are pointing backward
The error of pointing one's elbows backward is common. This will make you want to lean forward, causing back pain. Your elbows must be pointing downwards, and your shoulders should be brought back and pressed together. As an effect, your chest will remain upright.
2. You're neglecting your core
During a squat, your torso may not be the center of attention. Still, the poor upper-body technique can be detrimental. Your low back is vulnerable to damage when your back is rounded.
3. Squatting very low
According to some research, squatting low is beneficial to your health, but experts suggest only squatting 90 degrees.
Going beyond this point creates too much strain on your knees and quads, and you won't have enough strength to push up with your glutes. It may also raise the risk of lower back damage.
4. You sag your chest
A squat can be made or broken by good posture. Your cervical spine slopes upward, putting you at risk for disc injury.
Leaning too far forward, on the other hand, over-rounds the back and stresses the spin. Too many squat errors are caused by improper posture.
Of course, as you sit back and down into your squat, it's natural to lean forward a little. Make use of a mirror. You're on the right track if you can imagine yourself with your head straight and chest high.
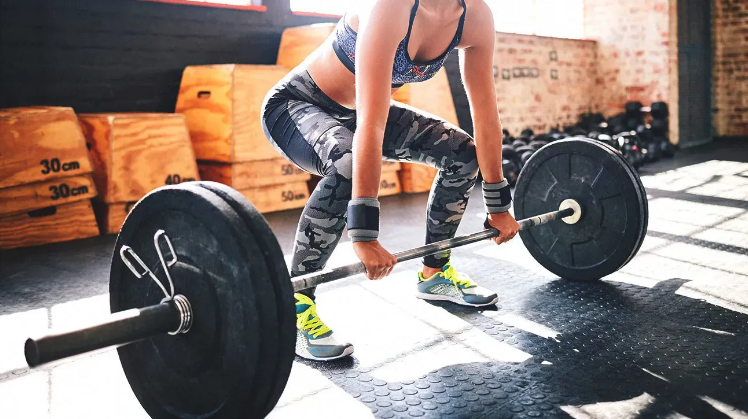
Proper Form
- Stand straight with your feet having a shoulder-width distance or slightly more expansive and your toes pointing forward or slightly outward. If you lack ankle mobility, a wider stance with slanted feet may be preferable. It's crucial to feel secure and at ease in this situation.
- Stand with your toes on a line to keep one foot from being in front of the other. Maintain square and level hips.
- Maintain a high chest and head. Keep a level neck position by looking directly ahead, not up or down.
- Engage your core muscles while pulling your shoulders back and down. Maintain a neutral spine during the movement by not leaning forward or rounding your back.
- Shift your weight from your forearms to your heels. To drop into a squat, bend your knees and hinge forward at the hips simultaneously.
- Throughout the exercise, keep your hips square, your torso erect, and your spine neutral. To get up, engage your pelvis and keep your heels steadily firm on the ground.
- Since this action is linked to knee pain, when you go down to a squat, your knees should be parallel to your toes, but not beyond them, and they should not collapse inward at any time.
- Strengthen your hip abductors initially if you can't keep your knees under control. Assuming there is an invisible barrier ahead of you, keep your nose, knees, and toes vertically aligned.
- According to Contreras, squat depth is accomplished through hip flexion and ankle dorsiflexion, not by rounding the spine.
- With proper form, you'll only be able to travel as far as your mobility allows. While some people can squat from their buttocks to their heels, that range of motion isn't typically required in outdoor activities.
- To shore up your weakness, concentrate on one component at a time, and if you have any doubts, consult a coach or trainer.
- As you practice, your form, awareness, and range of motion will steadily improve, allowing you to reach your full athletic potential.
Safety Tips
Tip #1: Maintain a straight gaze
It may be natural to glance down when executing a squat, but you should keep your gaze directly ahead. Pick an area in front of you to concentrate on to aid with this. This may assist you in maintaining a neutral neck position.
Tip #2: Maintain an upright posture
Avoid slouching your shoulders or arching your spine. Keep your spine erect and in a balanced position, and don't glance down or up with your head.
Tip #3: Lift enough weight you can handle
If your form can't take it, don't add too much weight. If you squat correctly, you'll gain more benefits than if you lift too much weight. Lifting excessive weight might potentially cause problems to your lower back, knees, and hips.
Benefits of Squats
1. Builds your muscle
Squats engage a large number of muscles. Your knees bend, your torso remains taut, and your upper body bears the bar’s weight. To balance and squat the weight, all of these muscles function together. This causes testosterone and other muscle-building hormones to be released. Your muscles develop more robust and more prominent as you squat greater weights.
2. Increases fitness
Squats help to strengthen your entire body, even your heart. It improves efficiency because every action requires less effort. A stronger heart is put under less stress when walking upstairs or running. Over time, your heart rate and blood pressure will decrease as a result of this. As a result, your cardiovascular fitness will improve. Unlike what some doctors may tell you, squatting is excellent for your heart.
3. Improves your balance
Squats teach you how to maintain balance while moving your body. Your balance and coordination will improve as a result of this exercise. It also enhances your sense of movement in space. Squats help you improve your athletic performance as well as your ability to pick up new skills. When walking upstairs or in the dark, they reduce the risk of falling. Machines should not be used for squats. Squat free weights to better your balance.
4. Burn fats
As your body expends more energy than you consume, you lose weight. When you lift weights, your muscles expend energy. Because they utilize more muscles and lift heavier weights, squats expend the most calories than any exercise. Heavy-weight squats enhance your body’s energy consumption for hours. When combined with correct nutrition, Squats will aid in fat loss and the development of six-pack abs.
5. Strengthen bones
When you squat, gravity drags the bar down. Everything beneath the bar is compressed. Bones are living structures that react to vertical compression by becoming stronger. Squats don't prevent you from gaining weight. Your bone density will improve as a result of them. They strengthen them and make them less brittle. Consequently, you are less likely to fall and get osteoporosis